Understanding Antioxidants
What Are Antioxidants?
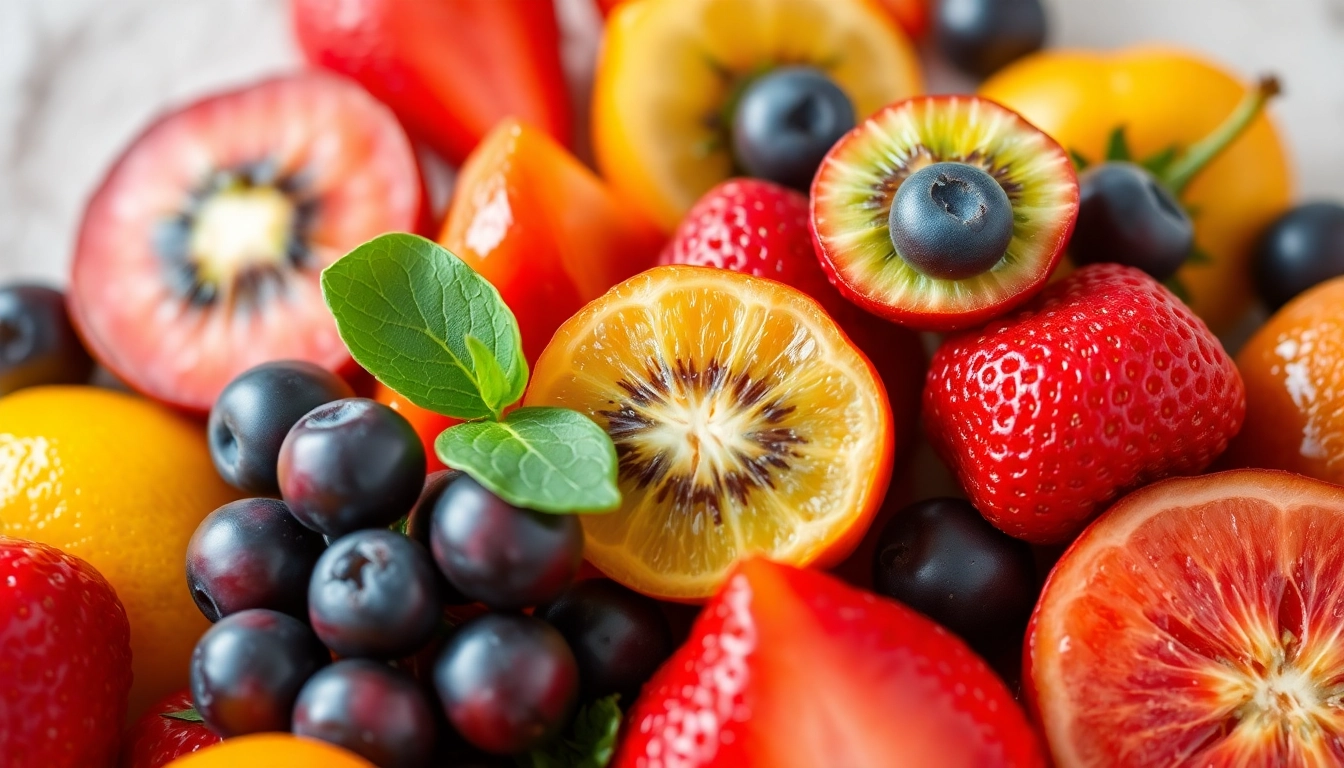
Antioxidants are naturally occurring compounds in various foods that play a crucial role in protecting our cells from oxidative stress. This oxidative stress is primarily caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules generated during metabolic processes like eating, exercise, and even breathing. These free radicals can damage cellular components, leading to numerous health issues, including aging, heart disease, and cancer. The primary function of antioxidants is to scavenge these free radicals, neutralizing their harmful effects and maintaining cellular integrity. Antioxidants are abundant in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains, making these foods essential for a balanced diet.
The Role of Antioxidants in Health
The significance of antioxidants extends beyond merely neutralizing free radicals. They are integral to numerous biological processes, including the modulation of inflammation, enhancement of immune responses, and the maintenance of overall cellular health. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and selenium contribute to preventing cellular damage, thereby playing a vital role in disease prevention. Numerous studies have linked a diet rich in antioxidants with lower incidences of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders and neurodegenerative conditions.
Natural vs. Supplemented Antioxidants
Antioxidants can be obtained from both dietary sources and supplements. However, emerging evidence suggests that the antioxidants derived from natural food sources tend to be more effective than their supplemented counterparts. Whole foods provide a complex matrix of nutrients and phytochemicals that work synergistically, enhancing the protective effects of antioxidants. In contrast, isolated antioxidant supplements may not deliver the same benefits and could lead to imbalances in the body. For optimal health, incorporating a variety of antioxidant-rich foods is recommended over reliance on supplements.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants and Disease Prevention
Research has shown a strong correlation between high antioxidant intake and reduced risk of chronic diseases. For instance, antioxidants may help combat cancer by protecting DNA cells from oxidative damage, a precursor to malignant transformations. Similarly, antioxidants such as flavonoids and carotenoids present in fruits and vegetables have been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. They improve endothelial function, lower blood pressure, and reduce inflammation, creating a heart-protective effect.
Impact on Aging and Longevity
As we age, our bodies’ ability to neutralize free radicals declines, leading to increased oxidative stress that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Antioxidants are regarded as a potential strategy to slow down these aging processes. Studies suggest that individuals who consume diets rich in antioxidants tend to have a decreased risk of age-related diseases and may experience improved longevity. Antioxidants like coenzyme Q10 and glutathione have shown promise in enhancing cellular energy production and maintaining cellular function as we age.
Promoting Skin Health with Antioxidants
Antioxidants also play a crucial role in skin health. They combat oxidative stress caused by environmental factors such as UV radiation, pollution, and smoking, which can lead to premature skin aging and other skin problems. Vitamin C, for example, is known for its skin-healing properties and is commonly found in skincare products due to its role in collagen synthesis and protection against sun damage. Regular consumption of antioxidant-rich foods can improve skin texture and may even reduce the risk of skin cancers.
Top Foods Rich in Antioxidants
Fruits and Vegetables: Nature’s Antioxidant Powerhouses
A variety of fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants. Berries, especially blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are among the highest in antioxidant content, thanks to their high levels of vitamin C and anthocyanins. Other fruits such as cherries, grapes, and oranges also contribute significantly to antioxidant intake. Leafy greens like kale and spinach, along with cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, are also excellent sources of antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress in the body.
Herbs and Spices with High Antioxidant Content
In addition to fruits and vegetables, many herbs and spices are rich in antioxidants. Turmeric, with its active ingredient curcumin, is renowned for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Other herbs, such as oregano, thyme, and rosemary, add not only flavor to dishes but also significant antioxidant benefits. Incorporating these herbs and spices into your meals can boost your overall antioxidant intake while enhancing the taste of your food.
Superfoods Loaded with Antioxidants
Superfoods are often marketed for their dense nutritional value, and many are high in antioxidants. Foods like matcha, acai berries, and dark chocolate (particularly those high in cocoa content) are celebrated for their antioxidant properties. Green tea, which contains catechins, is also a popular choice for its health benefits. Incorporating these superfoods into your diet can provide a concentrated source of antioxidants that support overall health and wellness.
Incorporating Antioxidants into Your Diet
Simple Recipes for Antioxidant-Rich Meals
Incorporating antioxidants into your diet can be simple and delicious. Consider starting your day with a berry smoothie blended with spinach, banana, and almond milk. For lunch, prepare a quinoa salad with cherry tomatoes, bell peppers, and a sprinkle of herbs such as parsley or cilantro. Dinner could feature grilled salmon seasoned with turmeric and served with steamed broccoli and roasted sweet potatoes. These meals not only offer a variety of antioxidants but also provide essential nutrients for overall health.
Choosing Antioxidant Supplements
If you choose to take antioxidant supplements, it’s essential to select high-quality products. Look for those that contain a blend of natural sources rather than isolated nutrients. Be cautious of mega-doses, as excessive intake of certain antioxidants can lead to imbalances and may even be harmful. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation can ensure you choose the right approach for your individual health needs.
Daily Tips for Boosting Antioxidant Intake
Increasing your daily antioxidant intake can be straightforward. Aim to fill half your plate with colorful fruits and vegetables at each meal. Opt for whole grains over processed grains, and incorporate a variety of nuts and seeds into your snacks. Drinking herbal teas and infusing water with fruits can also boost your antioxidant intake. Lastly, consider cooking with antioxidant-rich herbs and spices to enhance flavor and health benefits in your meals.
Research and Current Trends in Antioxidants
Recent Studies on Antioxidants and Health
Recent studies have continued to explore the expansive role of antioxidants in health and disease prevention. Research indicates that dietary antioxidants may support cognitive health, potentially delaying the onset of neurodegenerative diseases. A study in the journal Aging Cell found that diets high in antioxidant-rich foods correlate with improved cognitive function in older adults. Furthermore, ongoing research continues to uncover the mechanisms by which antioxidants affect cellular health and combat disease.
Future Research Directions
Future research will likely focus on uncovering the specific benefits of various types of antioxidants, including their interactions with other nutrients. The development of personalized nutrition plans may become a trending area, tailoring antioxidant intake to individual health profiles and genetic predispositions. Additionally, the exploration of new food sources rich in antioxidants, such as exotic fruits and lesser-known vegetables, may provide new avenues for enhancing public health through dietary modifications.
Myths and Facts About Antioxidants
Throughout the discourse on antioxidants, several myths have surfaced. A common misconception is that all antioxidants are universally beneficial in high doses, which is not true. Each antioxidant functions differently within the body, and more is not always better. Another myth is that supplements can replace antioxidants obtained from food; however, as discussed, the matrix of nutrients found in whole foods provides more than just isolated compounds. By debunking these myths, individuals can make informed decisions about their diets and supplement use.